HSI lab in collaboration with Wichita State University has been awarded an NSF grant to develop seamless and inclusive location-based services for communities
This project attempts to use a common technology infrastructure to simultaneously serve the auxiliary wayfinding needs of people with a broad range of disabilities. From a human-computer interaction perspective, the project advances knowledge in applying universal design principles towards accessing location-based services. From an economic analysis perspective, the project advances knowledge about the impact of economies of scope and scale in the feasibility and sustainability of accessibility technologies in small to medium-sized communities. Expected societal impacts from the project include the development of wayfinding technologies (and associated tech transfer) that provides people with disabilities and also the general population a useful tool to increase their independence, and thus, quality of life; and creation of a model for other similar future efforts (beyond wayfinding) to address the need for greater inclusivity in how various community-based services are accessed.
Jul, 2020
HSI lab has been awarded a grant from Safety through Disruption (Safe-D) University Transportation Center (UTC) to study the advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) in police vehicles
This project will investigate how ADAS features should adapt in situations of multi-tasking and what types of ADAS are most effective for improving driver safety. The outcomes will provide practical guidelines to automotive companies supplying police vehicles regarding effective ADAS features/types and can improve officer safety in police operations. This project addresses safety in the primary area of automated vehicles and secondary application areas of vehicle technology, planning for safety, and driver factors and interfaces.
May, 2020
Dr. Zahabi was featured in Medical Design Briefs as one of the leading women in engineering and science
Mar, 2022
HSI lab research was featured in KTVA news
Modern technology has enabled upper limb amputees to keep pace in a fast paced society. But there are still challenges.
Researchers at three universities are working to make those daily tasks for amputees simpler too — not only physically, but mentally as well.
Feb, 2020
HSI lab research was featured in KTVA news
Researchers are using virtual reality as well as a new driving simulator inside the Emerging Technologies Building.
Texas A&M Assistant Professor Maryam Zahabi and her team are studying computer models and machine learning algorithms. The scientists are also using the simulators to study tasks most of us find as very simple. They hope to give more guidance to engineers designing new prosthetic devices.
“So the objective of this study is to understand the cognitive load, or mental workload when prosthetic users use different types of upper limb prosthetic device. So the issue is that most of these prosthetic devices are actually very hard to use and very challenging,” said Zahabi, Ph.D.
Their work on improving prosthetics is being funded by the National Science Foundation. Texas A&M is partnering with North Carolina State University and the University of Florida for the study.
(For more information, click the title)
Feb, 2020
3 things you need to know about the new driving simulator
The Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at Texas A&M University installed a new driving simulator to use in research pertaining to driving, autonomous vehicles, and other vehicle technologies.
(For more information, click the title)
Jan, 2020
Algorithms improve prosthetics for upper limb amputees
Dr. Maryam Zahabi, assistant professor in the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at Texas A&M University, and her team are studying machine learning algorithms and computational models to provide insight into the mental demand placed on individuals using prosthetics. These models will improve the current interface in these prosthetic devices.
The researchers are studying prosthetics that use an electromyography-based human-machine interface. Electromyography (EMG) is a technique which records the electrical activity in muscles. This electrical activity generates signals that trigger the interface, which translates them into a unique pattern of commands. These commands allow the user to move their prosthetic device.
This research is a collaboration between Texas A&M, North Carolina State University and The University of Florida and is supported by the National Science Foundation.
(For more information, click the title)
Jan, 2020
HSI lab has been awarded a pilot project grant from North Carolina Occupational Safety and Health Education and Research Center (NC OSHERC)
HSI lab has been awarded a pilot project grant from North Carolina Occupational Safety and Health Education and Research Center (NC OSHERC) to develop an adaptive mobile computer terminal to improve police officers’ safety while driving.
Nov, 2019
HSI Lab has been awarded an NSF grant to study cognitive workload of electromyography (EMG)-based human-machine interfaces
HSI lab in collaboration with North Carolina State University (NCSU) biomedical engineering and University of Florida (UF) industrial and systems engineering departments were awarded a grant to study cognitive load of electromyography (EMG)-based human-machine interfaces (HMIs). The objective of this collaborative work is to identify differences in cognitive load between different EMG-based HMIs for systems supporting motor skill rehabilitation and activities of daily living for special populations.
Oct, 2019
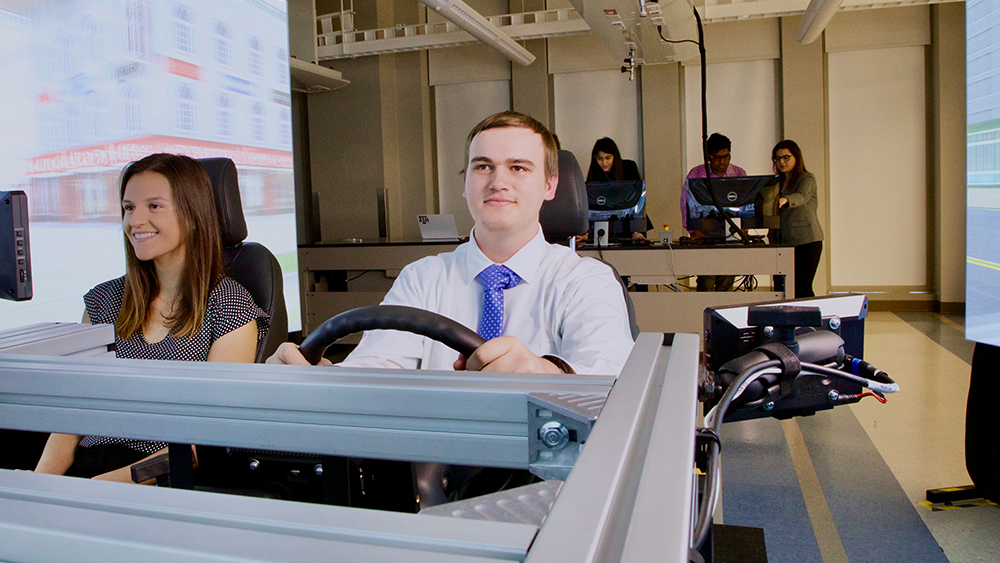
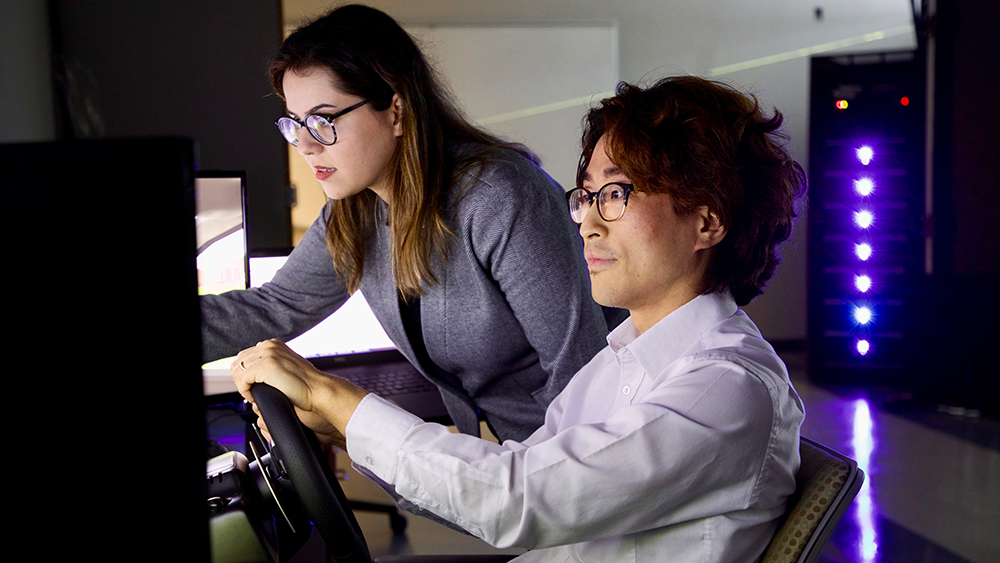
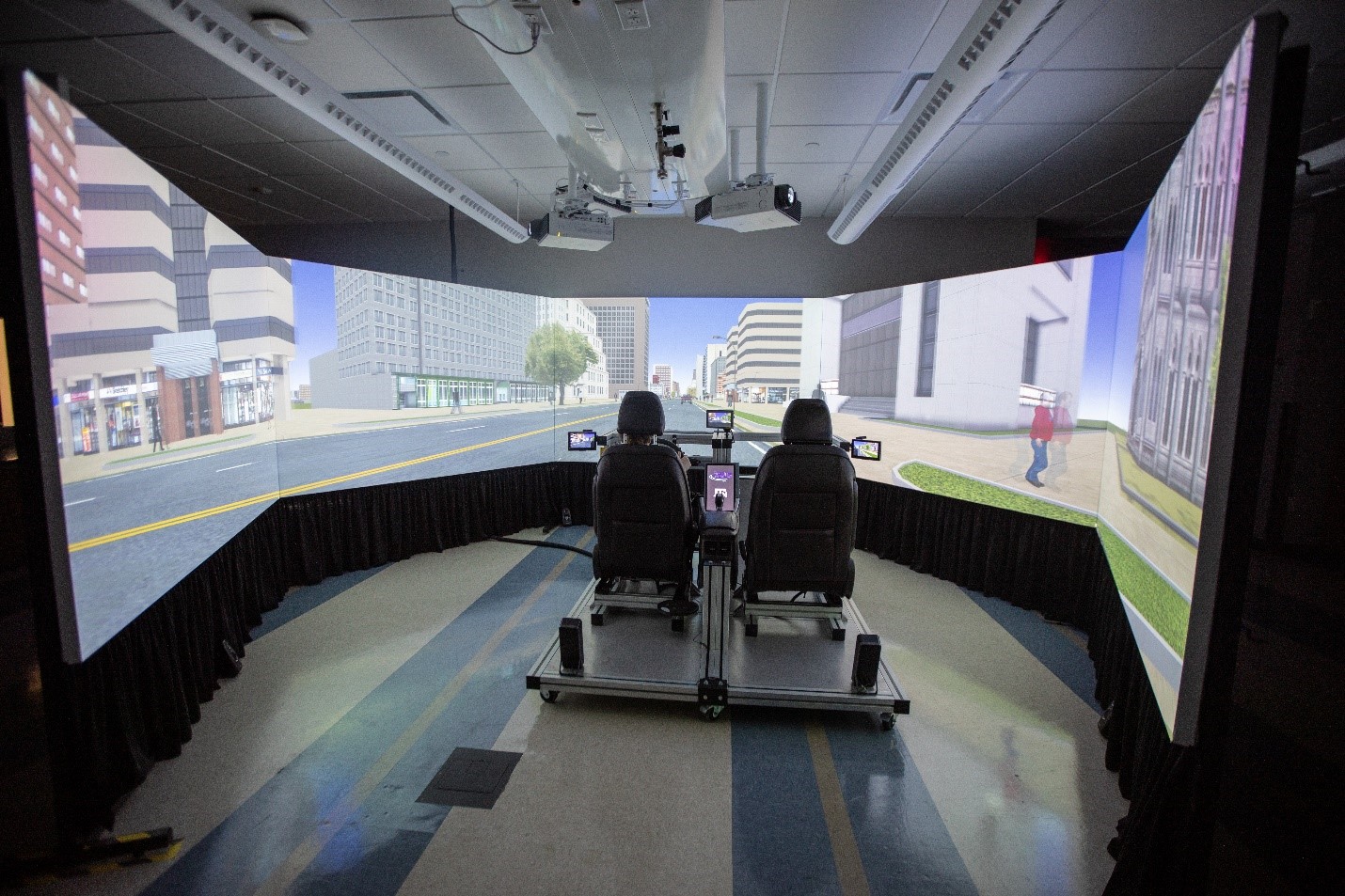
HSI lab in collaboration with HF&ML and HF&CS laboratories has purchased a state-of-the-art driving simulator!
Our driving simulator has 270 field of view (FOV) which very few simulators in the country can provide. This unique feature allows studying a wide range of surface transportation problems. In addition, the simulator is capable of modeling variety of simulations such as emergency vehicle interactions, autonomous vehicle control, different weather and visual conditions, etc. This is a high-fidelity driving simulator which provides a driving experience similar to real-world test environments. For more information regarding this simulator, please contact Dr. Maryam Zahabi at mzahabi@tamu.edu
Sep, 2019
HSI Lab was Awarded a T3 Grant to Study Emergency Responder Interactions with In-vehicle Technologies
HSI Lab in collaboration with Drs. Xudong Zhang (ISEN) and Stephen Crouse (health and Kinesiology) were awarded a T3 grant to study emergency response interactions with in-vehicle technologies. The objective of this study is to identify the most physically and cognitively demanding human-technology interactions in emergency vehicles using state-of-the-art biomechanical and cognitive performance modeling techniques.
Dec, 2018